English: PIA20021: Mystery Feature Evolves in Titan's Ligeia Mare
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20021
Original Caption Released with Image:
Figure 1 for PIA20021 Annotated Version
Figure 2 for PIA20021 Monochrome Version
High resolution monochrome TIFF file
(See Photojournal Note below for high resolution TIFF of main image)
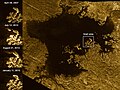
These images from the Radar instrument aboard NASA's Cassini spacecraft show the evolution of a transient feature in the large hydrocarbon sea named Ligeia Mare on Saturn's moon Titan.
Analysis by Cassini scientists indicates that the bright features, informally known as the "magic island," are a phenomenon that changes over time. They conclude that the brightening is due to either waves, solids at or beneath the surface or bubbles, with waves thought to be the most likely explanation. They think tides, sea level and seafloor changes are unlikely to be responsible for the brightening.
The images in the column at left show the same region of Ligeia Mare as seen by Cassini's radar during flybys in (from top to bottom) 2007, 2013, 2014 and 2015.
The bottom image was acquired by Cassini on Jan. 11, 2015, and adds another snapshot in time as Cassini continues to monitor the ephemeral feature (previously highlighted in PIA18430). The feature is apparent in the images from 2013 and 2014, but it is not present in other images of the region.
Cassini has observed similar transient features elsewhere in Ligeia Mare, and also in Kraken Mare (see PIA19047). These features are the first instances of active processes in Titan's lakes and seas to be confirmed by multiple detections. Their changing nature demonstrates that Titan's seas are not stagnant, but rather, dynamic environments.
The Cassini radar team plans to re-observe this particular region of Ligeia Mare one more time during Cassini's final close flyby of Titan in April 2017. The results may further illuminate the phenomenon responsible for the appearance of the transient features.
The large image panel shows Ligeia Mare in its entirety. Ligeia is Titan's second-largest liquid hydrocarbon sea, and has a total area of about 50,000 square miles (130,000 square kilometers), making it 50 percent larger than Lake Superior on Earth. This panel is a mosaic of five synthetic aperture radar images acquired by Cassini between 2007 and 2014. It shows a region approximately 330 by 305 miles (530 by 490 kilometers) in area.
An earlier version of the mosaic was released as PIA17031; the new version includes new data to fill in some gaps in coverage and to improve the quality of coverage in some of the previously imaged areas.
The images have been colorized and processed for aesthetic appeal. Labeled and monochrome versions of this image are also available.
The Cassini-Huygens mission is a cooperative project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the mission for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, DC. The Cassini orbiter was designed, developed and assembled at JPL. The radar instrument was built by JPL and the Italian Space Agency, working with team members from the United States and several European countries.
For more information about the Cassini-Huygens mission, visit http://www.nasa.gov/cassini and http://saturn.jpl.nasa.gov.
Photojournal Note: Also available is the
http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/tiff/PIA20021_full.tif full resolution TIFF file PIA20021_full.tif]. This file may be too large to view from a browser; it can be downloaded onto your desktop by right-clicking on the previous link and viewed with image viewing software.